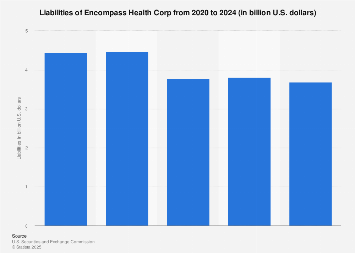
Encompass Health Corporation, a prominent player in the U.S. post-acute healthcare sector, faces a complex web of financial obligations as it navigates the evolving demands of patient care, regulatory environments, and capital markets. Understanding the company’s liability structure is crucial for investors, analysts, and stakeholders seeking to gauge its financial health and long-term sustainability. While precise, real-time liability figures often reside behind proprietary data walls, the broader context of Encompass Health’s financial architecture reveals a strategic approach to managing its debt and other financial commitments.
The healthcare industry, particularly the segment focused on rehabilitation and skilled nursing, is inherently capital-intensive. Encompass Health’s operational model, which involves owning and operating a vast network of inpatient rehabilitation hospitals and home health and hospice agencies, necessitates significant investment in infrastructure, technology, and skilled personnel. These investments, coupled with the ongoing costs of delivering care, inherently lead to a substantial liability profile.
Broadly speaking, a company’s liabilities can be categorized into current liabilities – those due within one year – and long-term liabilities, which are obligations extending beyond that timeframe. For a company like Encompass Health, current liabilities typically include accounts payable (money owed to suppliers and vendors), accrued expenses (costs incurred but not yet paid, such as salaries and benefits), and short-term debt obligations. Long-term liabilities, on the other hand, are dominated by long-term debt, deferred tax liabilities, and potentially pension obligations, though the latter has become less prevalent in recent years with the shift towards defined contribution plans.
Encompass Health’s long-term debt is a critical component of its liability structure. This debt is often incurred to finance acquisitions, fund capital expenditures for facility upgrades and expansion, and support general corporate purposes. The company’s ability to service this debt, indicated by metrics like its debt-to-equity ratio and interest coverage ratio, is a key determinant of its financial stability. Analysts meticulously track these ratios against industry benchmarks and historical trends to assess the company’s leverage and its capacity to meet its debt obligations without undue strain. For instance, a rising debt-to-equity ratio might signal increased financial risk, while a strong interest coverage ratio suggests ample operating income to cover interest payments.
The healthcare sector is subject to a stringent and ever-changing regulatory landscape. Reimbursement policies from government payers like Medicare and Medicaid, as well as private insurers, directly impact a company’s revenue streams and, consequently, its ability to manage liabilities. Fluctuations in reimbursement rates, changes in coding practices, or the implementation of new value-based care models can create financial pressures. Encompass Health, like its peers, must maintain robust compliance programs to avoid costly penalties and legal challenges, which can also manifest as significant liabilities, either through fines or settlement costs.
Moreover, the healthcare services market is characterized by intense competition. To maintain its market position and drive growth, Encompass Health often engages in strategic acquisitions. While these acquisitions can bolster its service offerings and geographic reach, they also frequently involve the assumption of debt or the issuance of new debt to finance the transactions. This M&A activity, while potentially value-accretive, directly influences the company’s overall liability profile. Careful due diligence and integration planning are paramount to ensure that acquired entities contribute positively to the company’s financial health rather than becoming a drag on its resources.
Market dynamics also play a significant role. The demand for post-acute care services is influenced by demographic trends, such as an aging population, and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases. These factors generally create a favorable demand environment for Encompass Health. However, economic downturns can impact patient volumes and payer mix, indirectly affecting the company’s liquidity and its capacity to manage its financial obligations. A robust liquidity position, often reflected in its current assets and access to credit lines, is therefore essential for weathering economic volatility.
Comparisons with other major players in the post-acute care sector, such as Kindred Healthcare (now part of Elevance Health) or Select Medical Holdings, can provide valuable insights into Encompass Health’s liability management strategies. While each company has its unique operational nuances and capital structures, analyzing their debt levels, liquidity ratios, and profitability can highlight industry best practices and potential areas for improvement. For example, a peer with a significantly lower debt-to-equity ratio might be employing a more conservative financing strategy, or conversely, might be foregoing growth opportunities that require leverage.
The economic impact of Encompass Health’s liability management extends beyond its own balance sheet. As a major employer and provider of essential healthcare services, its financial stability is crucial for the communities it serves. A healthy financial standing allows the company to invest in its workforce, maintain and upgrade its facilities, and continue to provide high-quality care, thereby contributing to local economies and public health outcomes. Conversely, significant financial distress could lead to service disruptions, job losses, and reduced access to care.
Looking ahead, Encompass Health, like the broader healthcare industry, faces ongoing challenges and opportunities. The increasing focus on value-based care, technological advancements in patient monitoring and treatment, and evolving reimbursement models will continue to shape the financial landscape. The company’s ability to effectively manage its liabilities – by optimizing its debt structure, maintaining strong operational performance, and adapting to regulatory and market shifts – will be central to its continued success and its capacity to fulfill its mission of improving the lives of patients in its care. Understanding the intricacies of its financial obligations is not merely an academic exercise but a critical element in assessing the resilience and future trajectory of this vital healthcare provider.