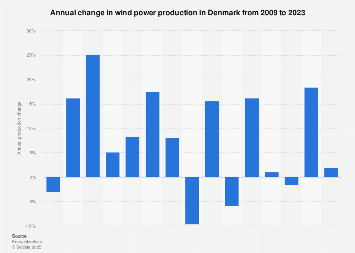
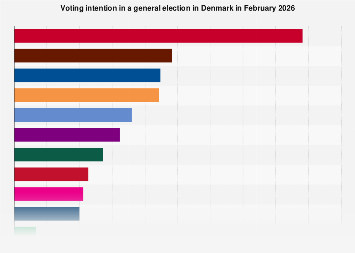
Copenhagen, Denmark – Denmark, a long-standing pioneer in renewable energy, particularly wind power, has registered a modest two percent increase in its wind energy production for 2023 compared to the preceding year. This incremental growth, while positive, underscores the complex interplay of factors influencing the nation’s decarbonization trajectory and its position within the broader global shift towards sustainable energy sources.
The latest figures, covering the period from 2009 to 2023, reveal a nuanced picture of Denmark’s wind energy evolution. While the recent year’s growth is consistent with a maturing renewable energy sector, historical data indicates periods of more dramatic expansion. The most significant surge in Danish wind power production occurred in 2011, when output saw an extraordinary percentage increase from the previous year, a testament to the nation’s early and ambitious commitment to harnessing wind resources. This historical peak highlights the rapid technological advancements and policy support that characterized the initial phase of Denmark’s wind energy development.
Globally, the energy landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by climate imperatives, energy security concerns, and technological innovation. Denmark’s experience is part of this larger narrative. As of the latest available data, wind energy continues to be a cornerstone of the Danish electricity supply, often contributing a substantial portion of the nation’s total power generation. This reliance positions Denmark as a benchmark for other countries seeking to integrate large-scale renewable energy into their grids.
The two percent growth in 2023, while seemingly small, represents a considerable volume of energy when considering the scale of Denmark’s wind infrastructure. This growth can be attributed to several factors, including the commissioning of new wind farms, upgrades to existing turbines, and improved operational efficiency. However, it also reflects the challenges inherent in scaling up renewable energy projects, such as grid integration, permitting processes, and the intermittency of wind resources.
In a global context, Denmark’s renewable energy penetration is among the highest. Countries like Sweden, Norway, and Portugal have also made significant strides in deploying wind power, with varying degrees of success and reliance on other renewable sources like hydropower. The International Energy Agency (IEA) consistently reports on the growing global capacity of wind power, emphasizing its critical role in achieving net-zero emissions targets. For instance, global wind power capacity has seen consistent year-on-year increases, driven by supportive government policies, declining technology costs, and corporate sustainability commitments. The expansion in 2023 across major markets like China, the United States, and European nations, collectively contributes to a robust global growth trend, making Denmark’s contribution, though incremental, a significant part of this larger picture.
The economic implications of wind power development are multifaceted. For Denmark, the sector represents a significant source of employment, technological innovation, and export opportunities in wind turbine manufacturing and related services. The continued investment in wind energy infrastructure stimulates economic activity and contributes to energy independence, reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. Furthermore, the predictable, albeit variable, nature of wind power helps to stabilize energy prices in the long term, offering a hedge against the volatility of global fossil fuel markets.
However, the sustained expansion of wind power is not without its economic considerations. The upfront capital investment for offshore and onshore wind farms remains substantial. Ensuring grid stability and reliability in the face of increasing renewable energy penetration requires significant investment in grid modernization, energy storage solutions, and smart grid technologies. Denmark, like many other leading nations, is actively exploring and investing in these areas to complement its wind power generation. Battery storage, pumped hydro, and hydrogen production are increasingly seen as vital components of a future-proof energy system that can effectively manage the variability of wind and solar power.
Market analysis suggests that the global wind energy market is projected for continued strong growth in the coming years, driven by ambitious climate targets and increasing investor confidence. Forecasts indicate a steady expansion of both onshore and offshore wind capacity, with offshore wind expected to play an increasingly dominant role due to its higher capacity factors and the availability of suitable sites. Denmark, with its established expertise and infrastructure, is well-positioned to capitalize on these global trends, potentially through further development of its own resources and by exporting its technological know-how.
The Danish government has consistently set ambitious targets for renewable energy deployment, aiming to achieve a fully decarbonized energy system. While the two percent growth in wind power production in 2023 indicates progress, achieving these long-term goals will likely necessitate accelerated deployment rates and continued policy innovation. This includes streamlining permitting processes, incentivizing further investment, and fostering public acceptance of renewable energy projects. The success of Denmark’s renewable energy agenda will not only impact its domestic economy and environment but will also serve as a crucial case study for other nations navigating their own energy transitions. The nuanced performance in 2023 serves as a reminder that while the direction is clear, the pace and scale of the energy transition are shaped by a complex array of economic, technological, and political forces.