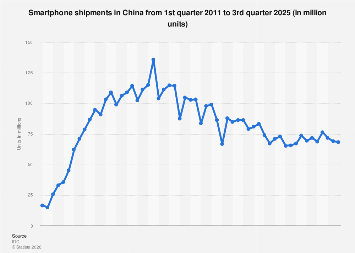
In the third quarter of 2025, China’s bustling smartphone market experienced a noticeable contraction, with approximately [Insert Estimated Figure Here] million units shipped. This figure represents a sequential decline from the preceding quarter and a year-over-year decrease compared to the same period in 2024, signaling a period of recalibration for the world’s largest mobile device arena.
The trajectory of China’s smartphone shipments since 2011 has been one of remarkable ascent, culminating in a robust figure of over [Insert Estimated Figure Here] million units dispatched in 2022. This sustained growth cemented China’s position not only as a colossal consumer market but also as a critical hub for global smartphone production and distribution. In 2019 alone, China accounted for a commanding [Insert Estimated Percentage Here] percent of all smartphone shipments worldwide, underscoring its indispensable role in the international technology landscape. While recent quarterly data suggests a temporary deceleration, the overarching forecast remains that China will continue to wield significant influence and leadership in the global smartphone arena.
The penetration of smartphones within China’s vast mobile user base is nearing saturation. By 2023, an estimated [Insert Estimated Percentage Here] percent of Chinese mobile phone users were projected to be utilizing smartphones. This translates into a substantial user base, with one billion individuals actively engaged with smartphones in China in 2022. The growth in smartphone adoption, though perhaps moderating in its pace, is still poised to expand. Projections indicate that the number of Chinese smartphone users will inch closer to the [Insert Estimated Figure Here] billion mark by 2027, a testament to the enduring appeal and indispensable nature of these devices in daily life.
The competitive landscape among smartphone manufacturers within China is dynamic and fiercely contested. For a significant period, Huawei stood as the dominant local brand, consistently leading in shipment volumes. At its zenith in 2019, the company was responsible for shipping in excess of [Insert Estimated Figure Here] million units, a formidable achievement that showcased its technological prowess and market penetration. However, the ensuing years saw a significant shift, with Huawei being an exception among major vendors in experiencing a substantial erosion of its market share. In contrast, rivals such as Oppo and Vivo have demonstrated resilience and strategic acumen, steadily capturing a larger portion of the market. This redistribution of market power reflects evolving consumer preferences, supply chain dynamics, and the impact of geopolitical factors on the industry.
On the software front, the dominance of Google’s Android operating system in China remains largely unchallenged. Android commands a substantial market share, exceeding [Insert Estimated Percentage Here] percent, reflecting its widespread adoption across a diverse range of manufacturers and device price points. While Apple’s iOS holds a respectable position, accounting for approximately [Insert Estimated Percentage Here] percent of the smartphone operating system market in China, it operates within a distinct premium segment. This bifurcation in the OS market highlights the strategic positioning of both platforms, catering to different consumer segments and technological ecosystems.
The current slowdown in Chinese smartphone shipments can be attributed to a confluence of factors. Global economic uncertainties, including persistent inflation and rising interest rates, are dampening consumer discretionary spending across many regions, and China is not immune. Supply chain disruptions, while easing from their pandemic-induced peaks, can still affect production and lead times, impacting the availability and cost of devices. Furthermore, the domestic market is highly mature, with a significant portion of the population already owning smartphones. This leads to a replacement-driven market, where upgrade cycles may lengthen as consumers hold onto their devices for longer, especially if there isn’t a compelling perceived leap in innovation or value.
Industry analysts point to several key trends shaping the future of the Chinese smartphone market. The foldable phone segment, while still nascent, is gaining traction, offering a premium and innovative product category for early adopters and high-spending consumers. 5G adoption continues to be a significant driver, with manufacturers prioritizing devices that leverage the faster speeds and lower latency of the latest mobile network technology. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into smartphone features, from enhanced camera capabilities to personalized user experiences, is also becoming a critical differentiator.
Looking ahead, the interplay between domestic innovation and global market dynamics will be crucial. Chinese brands are increasingly investing in research and development, aiming to create devices that not only compete on price but also on cutting-edge technology and sophisticated design. The government’s focus on technological self-sufficiency and advanced manufacturing may also provide a supportive environment for local players. However, international market access and trade relations will continue to be significant variables.
The economic implications of this market dynamic extend beyond the device manufacturers themselves. The smartphone industry is a major employer and a significant contributor to China’s export economy. A sustained downturn in shipments could have ripple effects on component suppliers, retail networks, and the broader technology ecosystem. Conversely, a resurgence driven by new product cycles, improved economic conditions, or the successful expansion of Chinese brands into international markets could reignite growth.
As the Chinese smartphone market navigates this period of adjustment, its sheer scale and the continued evolution of mobile technology ensure its ongoing relevance on the global stage. The ability of manufacturers to innovate, adapt to changing consumer demands, and effectively manage global economic headwinds will determine the pace and direction of its future growth. The coming quarters will be a key indicator of whether the recent dips represent a temporary recalibration or a more fundamental shift in the market’s long-term expansion.