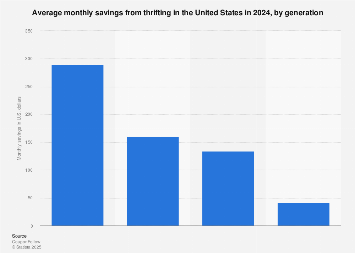
A significant economic shift is underway in the United States, as a growing number of consumers, spanning various age demographics, are turning to the secondhand market to stretch their budgets. New data from a 2024 survey reveals distinct patterns in how much different generations are saving through thrifting, highlighting the evolving consumer landscape and the increasing financial prudence driven by economic pressures and a desire for sustainable consumption.
The survey, conducted in October 2024 among 1,000 U.S. respondents, indicates that Generation Z is leading the charge in maximizing savings through the purchase of pre-owned goods. This demographic, often characterized by its digital nativity and heightened awareness of economic realities, reports the highest average monthly savings from thrifting. While precise figures are restricted to premium subscribers, the data suggests that Gen Z is realizing substantial financial benefits, underscoring their strategic approach to personal finance in an era of rising inflation and economic uncertainty. This generation’s engagement with secondhand markets is not merely about cost savings; it often intertwines with a commitment to environmental sustainability and a rejection of fast fashion’s disposable culture. Their embrace of platforms like Depop, Poshmark, and local thrift stores reflects a broader trend towards conscious consumerism, where value is derived not just from the price tag but also from the ethical and environmental implications of purchasing decisions.
In contrast, older generations appear to be realizing more modest, though still significant, savings. Baby Boomers, a generation that has experienced various economic cycles throughout their lives, report considerably lower average monthly savings from secondhand shopping compared to their younger counterparts. This disparity may be attributed to a variety of factors, including differing shopping habits, established brand loyalties, and potentially less familiarity or comfort with the online and physical infrastructure of the modern secondhand market. However, even these lower savings represent a tangible financial advantage, suggesting that thrifting offers a universally accessible strategy for cost reduction. The economic pressures faced by all age groups in recent years, from housing costs to everyday expenses, are likely compelling even those less inclined towards thrifting to explore its benefits.
The broader implications of these generational savings patterns are multifaceted. For retailers, the data signals a continuing evolution in consumer demand. Brands that can effectively integrate sustainable and secondhand options into their business models, or those that cater directly to the thrifting market, are poised for growth. This includes not only traditional thrift stores but also a burgeoning ecosystem of online resale platforms, consignment shops, and peer-to-peer marketplaces. The success of these ventures is directly tied to their ability to attract and retain customers across different age groups, offering a compelling value proposition that balances price, style, and sustainability.
Economically, the rise of the secondhand market contributes to a more circular economy, diverting waste from landfills and reducing the demand for new resource extraction and manufacturing. This has positive ripple effects on environmental sustainability, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change and reduce pollution. Furthermore, the growth of the resale industry creates new employment opportunities in areas such as inventory management, authentication, repair, and digital platform development. The financial savings realized by consumers can then be reallocated to other areas of spending, potentially boosting local economies and supporting other businesses.
Market research consistently points to the robust growth of the global apparel resale market, projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars in the coming years. This expansion is fueled by a confluence of factors, including increased consumer awareness of sustainability, the desire for unique and affordable fashion, and the growing acceptance of pre-owned goods as a viable and desirable alternative to new items. The U.S. market, being one of the largest consumer economies, plays a pivotal role in this global trend.
The survey’s methodology, involving 1,000 respondents over a two-day period in October 2024, provides a snapshot of current consumer sentiment and behavior. While the exact financial figures for each generation are subject to subscription access, the qualitative findings underscore a clear generational divergence in savings achieved through secondhand shopping. This data is invaluable for businesses seeking to understand consumer motivations and tailor their strategies accordingly. It suggests that while Gen Z might be the most active participants in maximizing thrift savings, the underlying economic imperative is broad-based, encouraging a wider adoption of pre-owned goods across the demographic spectrum.
The increasing financial literacy and resourcefulness demonstrated by younger generations, particularly Gen Z, in leveraging secondhand markets for significant savings is a testament to their adaptability. They are not only responding to economic pressures but also actively shaping a more sustainable and value-conscious consumption paradigm. As this trend matures, and as older generations become more integrated into the secondhand ecosystem, the overall economic impact of thrifting in the United States is likely to grow, further solidifying its position as a significant and sustainable sector within the broader retail landscape. The ability of consumers to find significant monthly savings through thrifting is a compelling indicator of economic resilience and a forward-thinking approach to personal finance in an ever-changing global market.