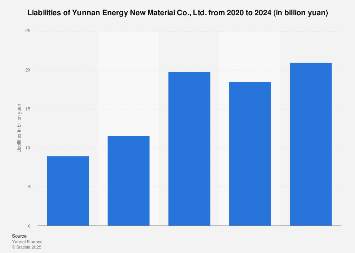
Yunnan Energy New Material Co., Ltd. is navigating a complex financial landscape characterized by an increasing burden of liabilities, a trend that warrants close examination within the context of China’s rapidly evolving new energy sector. While precise, real-time figures often remain proprietary or require premium access, available indicators and broader industry trends suggest a significant rise in the company’s financial obligations as it expands its operations and capitalizes on burgeoning market demand for advanced materials crucial to the green energy transition. This escalating debt profile is not an isolated phenomenon but reflects the substantial investment requirements inherent in scaling production, developing new technologies, and securing a competitive edge in a sector experiencing exponential growth and intense competition.
The company’s core business revolves around the production of critical materials for lithium-ion batteries, including cathode materials and other battery components. The global surge in electric vehicle (EV) adoption and the expansion of renewable energy storage solutions have created an unprecedented demand for these components. For instance, the International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that global EV sales could reach 35 million units by 2030, a substantial increase from the 10 million sold in 2022. This exponential growth directly translates into a heightened need for raw materials and advanced manufacturing capabilities, placing companies like Yunnan Energy New Material at the forefront of a vital industrial supply chain.
However, meeting this demand necessitates significant capital expenditure. The construction and expansion of state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, the research and development of next-generation battery chemistries, and the procurement of raw materials, such as lithium, nickel, and cobalt, all carry substantial price tags. Companies often resort to a mix of equity financing and debt to fund these ambitious expansion plans. Therefore, an increase in liabilities for Yunnan Energy New Material is likely a direct consequence of strategic investments aimed at bolstering its production capacity and technological prowess to capture a larger share of this lucrative global market.
Analyzing the potential drivers behind these growing liabilities requires understanding the specific segment of the new energy market Yunnan Energy New Material operates within. The cathode material sector, for example, is highly competitive and technologically intensive. Developing and mass-producing advanced cathode materials like nickel-rich ternary or lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries demands considerable R&D investment. Furthermore, securing a stable and cost-effective supply of precursor materials, often sourced from global markets subject to price volatility, can also necessitate forward contracts or financing arrangements that contribute to a company’s debt.
Market data from industry analysts often highlights the capital intensity of the battery materials sector. Reports frequently indicate that leading battery material producers are undertaking multi-billion-dollar expansion projects. For Yunnan Energy New Material, this translates into a need to finance new production lines, upgrade existing infrastructure, and potentially acquire new technologies or companies to enhance its vertical integration or product portfolio. These large-scale projects are typically financed through a combination of bank loans, corporate bonds, and other forms of debt financing.
The global economic environment also plays a crucial role. Rising interest rates in many major economies, including China, can increase the cost of borrowing, making debt financing more expensive. Companies that have taken on substantial debt may face higher interest payments, impacting their profitability and cash flow. This necessitates careful financial management and strategic debt restructuring to mitigate risks. Furthermore, geopolitical tensions and trade policies can affect the cost and availability of raw materials, adding another layer of complexity to financial planning.
Beyond operational expansion, liabilities can also arise from mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activities. In the fast-paced new energy sector, companies often pursue M&A to gain access to new markets, technologies, or raw material sources. If Yunnan Energy New Material has engaged in such activities, the associated debt taken on to finance these deals would contribute to its overall liability profile. For example, acquiring a competitor or a supplier could provide immediate market share or supply chain security but would also require significant financial backing.
The sustainability of this increasing liability burden is a key concern for investors and analysts. While debt can be a powerful tool for growth, an excessively high debt-to-equity ratio or a significant increase in short-term liabilities can signal financial distress. Investors will closely monitor Yunnan Energy New Material’s ability to service its debt obligations, its cash flow generation, and its profitability. Key financial ratios, such as the interest coverage ratio and the debt service coverage ratio, will be crucial in assessing the company’s financial health.
Comparatively, other major players in the global new energy materials market often exhibit similar trends of significant capital investment and, consequently, substantial debt. Companies in South Korea, Japan, and Europe that are also heavily involved in battery material production face comparable pressures to scale up rapidly to meet global demand. The difference often lies in their financing structures, access to capital markets, and government support. China’s new energy sector has benefited from strong state backing, which can influence the availability and cost of debt for domestic companies.
The economic impact of Yunnan Energy New Material’s financial strategy extends beyond the company itself. As a significant producer of essential battery components, its operational stability and financial health are critical for the broader EV and renewable energy industries. Disruptions in its supply chain or financial difficulties could have ripple effects, potentially slowing down the production of electric vehicles or the deployment of energy storage systems. This underscores the systemic importance of companies operating in this foundational sector.
Furthermore, the company’s ability to manage its liabilities effectively will influence its capacity for future innovation and expansion. A heavy debt load can constrain a company’s financial flexibility, making it more difficult to invest in cutting-edge research and development or to pursue new growth opportunities. Conversely, a well-managed debt structure can fuel rapid expansion, allowing the company to solidify its market position and contribute to the global energy transition. Investors and stakeholders will be keen to see how Yunnan Energy New Material balances its growth ambitions with prudent financial stewardship in the years to come. The company’s financial obligations, therefore, are not merely accounting figures but represent strategic choices and the inherent risks and rewards of operating in one of the world’s most dynamic and capital-intensive industries.