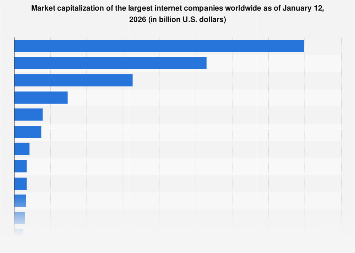
As of mid-January 2026, the landscape of global internet commerce is unequivocally dominated by a handful of tech behemoths, with Alphabet, the parent entity of Google, commanding the largest market capitalization worldwide. This digital colossus has solidified its position at the apex of the internet industry, a testament to decades of innovation and strategic expansion. Trailing closely behind, Amazon continues to exert immense influence across e-commerce and cloud computing, holding the second-largest market capitalization. The sheer scale of these enterprises underscores a significant shift in global economic power, with digital platforms now serving as central engines of growth and innovation.
The genesis of the modern internet economy can be traced back to the late 1990s in the United States, a period characterized by the explosive emergence of "dot-com" companies. These nascent online ventures, often born from ambitious ideas and a nascent understanding of the commercial potential of the World Wide Web, were emblematic of a transformative technological wave. The suffix ".com," derived from "commercial," became synonymous with this new breed of businesses. While many of these early pioneers succumbed to the speculative excesses and subsequent bursting of the dot-com bubble, a select few not only weathered the storm but evolved into global powerhouses. American giants like Amazon (established in 1994), Google (founded in 1998), and eBay Inc. (founded in 1995) represent enduring legacies of this era. Alongside them, the Chinese e-commerce titan Alibaba, also founded in 1998, has emerged as a formidable international player, reshaping the global digital marketplace.
Alphabet’s ascent to the pinnacle of the internet industry is a narrative rooted in academic research that rapidly transitioned into commercial success. What began as a doctoral project at Stanford University ultimately blossomed into Google, the world’s dominant search engine. Its pervasive market share in search, exceeding a significant percentage, has provided a robust foundation for its expansive ecosystem. Beyond its core search functionality, Google has strategically diversified its offerings through a series of high-profile acquisitions and organic development. Its portfolio now encompasses the ubiquitous video-sharing platform YouTube, the vast digital marketplace of the Google Play Store, the widely used webmail service Gmail, and the popular web browser Google Chrome, among numerous other services. This strategic integration has created a powerful network effect, further cementing its market leadership. In October 2015, a significant corporate restructuring saw Google reorganize under a newly formed parent company, Alphabet Inc., a multinational conglomerate designed to manage its diverse and rapidly growing ventures more effectively.
Beyond market valuation, the sheer scale of human capital employed by these digital leaders is also a critical indicator of their influence. As of early 2026, Amazon, Alphabet, and Alibaba stand out as the largest internet companies in terms of workforce size. This extensive employment base reflects the vast operational scope of these companies, spanning product development, logistics, customer service, research and development, and global market expansion. The employment figures are not merely statistical data points; they represent significant contributions to national economies through job creation, talent development, and the fostering of innovation within their respective regions and across the globe. The concentration of talent within these organizations also signifies a critical nexus of expertise, driving forward the technological frontiers of the digital age.
The global economic impact of these internet behemoths extends far beyond their immediate financial performance. They are instrumental in shaping consumer behavior, driving digital transformation across industries, and influencing international trade dynamics. The digital infrastructure they have built, from cloud computing services to online marketplaces, forms the backbone of modern commerce. For instance, Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading provider of cloud computing, powering a significant portion of the internet’s infrastructure and enabling countless smaller businesses to operate and scale without substantial upfront investment in physical hardware. Similarly, Google’s advertising platform underpins a vast segment of online marketing, providing revenue streams for content creators and facilitating targeted advertising for businesses of all sizes. Alibaba’s ecosystem, particularly in China, has revolutionized retail and payments, creating a deeply integrated digital economy.
Analyzing market capitalization trends reveals a persistent growth trajectory for these tech giants, even amidst broader economic fluctuations. While specific figures are subject to daily market volatility, the sustained dominance of Alphabet and Amazon suggests a robust demand for their services and a strong investor confidence in their future growth prospects. This confidence is often fueled by ongoing investments in artificial intelligence, machine learning, quantum computing, and other cutting-edge technologies, positioning them to define the next wave of digital innovation. The ability of these companies to consistently innovate and adapt to evolving consumer needs and technological advancements has been a key factor in their enduring success.
Comparisons with other major global economies highlight the unique position of the United States and China as hubs for these leading internet enterprises. While Europe and other regions have their own significant technology sectors and innovative companies, the sheer scale and market dominance of Alphabet, Amazon, and Alibaba remain unparalleled. This concentration of power raises important discussions about market competition, regulatory oversight, and the potential for monopolies. Governments worldwide are increasingly grappling with how to balance fostering innovation with ensuring a fair and competitive digital marketplace. The regulatory landscape surrounding data privacy, antitrust concerns, and digital taxation is evolving rapidly, reflecting the profound societal and economic influence of these companies.
The sustained growth of these internet titans is not without its challenges. Emerging markets present both opportunities for expansion and unique operational hurdles, requiring companies to adapt their business models to local contexts and consumer preferences. Furthermore, geopolitical tensions and trade policies can impact global operations and supply chains. The ongoing evolution of digital technologies, such as the metaverse, decentralized finance, and advanced AI, also presents both immense opportunities and potential disruptions. The companies that can successfully navigate these complex and dynamic environments will likely continue to shape the future of the global digital economy. The early months of 2026 serve as a snapshot of a continuously evolving landscape, where the giants of today are constantly striving to secure their positions for the challenges and opportunities of tomorrow.