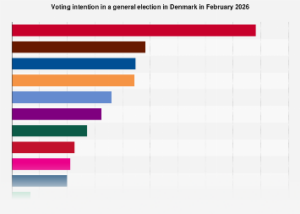
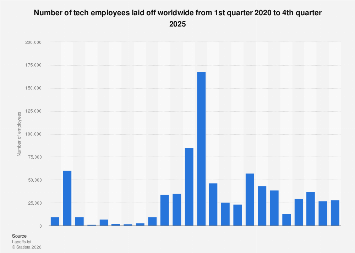
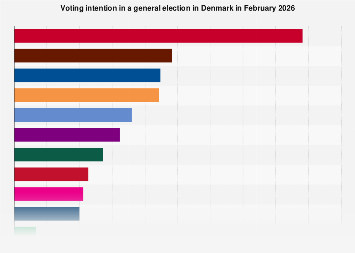
The global technology industry has navigated a turbulent period throughout 2025, marked by a significant wave of workforce reductions that has reshaped the landscape for both established giants and burgeoning startups. This trend, which escalated dramatically in the early months of 2023, saw the sector’s employment figures shrink at an alarming rate, with millions of professionals finding themselves displaced. While the immediate catalyst for this recalibration can be traced to a period of rapid expansion during the COVID-19 pandemic, the ongoing economic climate and the accelerating integration of artificial intelligence suggest that these workforce adjustments may extend well beyond the initial surge.
The first quarter of 2023 proved to be a watershed moment, with the technology sector recording an unprecedented surge in layoffs. Figures indicate that hundreds of thousands of employees across the globe were affected during this period alone. This widespread retrenchment was not confined to smaller entities; it permeated the very core of the industry, impacting the world’s most prominent technology conglomerates. Names synonymous with innovation and global reach, including Google, Microsoft, Meta, and IBM, all implemented substantial workforce reductions, contributing significantly to the overall bleak employment statistics. Amazon, in particular, distinguished itself by conducting multiple rounds of layoffs, affecting a larger number of employees than many of its peers within the global tech arena. The ripple effects of these decisions extended across a diverse range of industry verticals. Consumer-facing technology, hardware manufacturing, the food tech sector, and even the critical healthcare technology segment experienced considerable job losses. Beyond the behemoths, a litany of other prominent companies, from the rapidly scaling food delivery service Flink and online travel giant Booking.com to ride-sharing pioneer Uber, payment processor PayPal, professional networking platform LinkedIn, and fitness equipment innovator Peloton, also implemented significant staff cuts, underscoring the pervasive nature of this industry-wide correction.
The genesis of this widespread downsizing can be largely attributed to an aggressive period of overhiring that characterized the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. As global lockdowns spurred an exponential demand for digital services, from e-commerce and remote work solutions to entertainment and communication platforms, technology companies responded by rapidly scaling their operations and, consequently, their workforces. This expansion was viewed as a necessary strategic imperative to capitalize on a perceived permanent shift in consumer behavior and business practices. However, the post-pandemic reality proved more nuanced. As restrictions eased and the initial surge in demand began to moderate, coupled with persistent global economic uncertainties, including rising inflation and interest rate hikes, companies were compelled to re-evaluate their operational footprints and financial projections. This strategic reassessment inevitably led to a widespread realization that many had expanded too aggressively, creating an unsustainable cost structure. By the close of 2022, the cumulative effect of these adjustments had resulted in a record number of redundancies across the global tech sector, signaling the end of an era of seemingly unchecked growth.
Looking ahead, the trajectory of technology sector employment is increasingly intertwined with the rapid advancements and integration of artificial intelligence (AI). The potential impact of AI on the workforce is a subject of intense debate and considerable speculation among economists and industry leaders. AI-driven automation possesses the inherent capability to streamline and, in some cases, entirely replace tasks that were previously performed by human employees. This can lead to significant efficiencies and cost savings for businesses, but it also raises concerns about potential workforce redundancies on a scale that could dwarf previous layoff cycles. From AI-powered chatbots that are increasingly capable of handling complex customer service inquiries, thereby reducing the need for human call center agents, to sophisticated predictive algorithms that optimize supply chains and logistics, thereby minimizing the requirement for human oversight and intervention, the pursuit of enhanced efficiency and reduced operational expenditure is a potent driver for AI adoption. The question is not whether AI will impact the tech workforce, but rather the magnitude and nature of that impact, and whether the industry can foster new roles and opportunities at a pace commensurate with the displacement of existing ones.
The economic implications of these ongoing workforce adjustments are multifaceted. On one hand, significant layoffs can lead to a surge in unemployment within specific highly skilled demographics, potentially creating social and economic strain in regions heavily reliant on the tech industry. This can also lead to a "brain drain" as displaced talent seeks opportunities elsewhere. However, from a macroeconomic perspective, a recalibration of the tech sector’s cost base can lead to greater financial stability and profitability for companies, which can, in turn, foster reinvestment in research and development, innovation, and sustainable growth. Furthermore, the increased availability of experienced tech talent at potentially more competitive compensation levels could spur the growth of new ventures and accelerate the adoption of cutting-edge technologies by a broader spectrum of industries. The long-term impact will likely depend on a delicate balance between the efficiency gains offered by automation and the industry’s ability to cultivate new avenues for human ingenuity and employment. As the technology sector continues to evolve, the dynamic interplay between human capital and artificial intelligence will undoubtedly define its future and the livelihoods of those who power its innovation.