The landscape of international work and travel is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the burgeoning digital nomad movement. As more professionals embrace remote work, a growing number of nations are actively cultivating this trend by introducing specialized digital nomad visas. This proactive policy shift, poised for significant expansion by 2025, represents not merely an accommodation of a lifestyle choice, but a strategic economic imperative for countries seeking to attract talent, boost tourism, and diversify their economies in an increasingly interconnected world.
The proliferation of these visas is a testament to the evolving nature of work. Fueled by advancements in communication technology and a growing preference for flexibility, individuals are no longer tethered to a single physical office. This has created a global pool of mobile talent, capable of contributing to economies without necessarily being residents. Governments, recognizing this potential, are strategically positioning themselves to capture a share of this lucrative demographic. Early adopters of digital nomad visa programs have already witnessed tangible benefits, from increased demand for short-term and long-term accommodation to a stimulated local service economy.
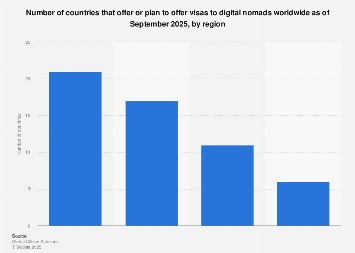
Examining the geographical distribution of these initiatives reveals a dynamic global competition. While Europe has been a prominent early mover, with countries like Croatia, Portugal, and Spain actively promoting their digital nomad offerings, other regions are rapidly catching up. Asia, with its burgeoning tech hubs and attractive cost of living in certain locales, is witnessing a surge in interest. Countries such as Thailand, Bali (Indonesia), and Vietnam have been building on existing tourism infrastructure to cater to remote workers. Latin America, too, is emerging as a significant player, with nations like Colombia, Mexico, and Costa Rica implementing visa programs designed to lure digital nomads with their vibrant cultures and affordable lifestyles.
The economic rationale behind these visa programs is multifaceted. Firstly, digital nomads inject foreign currency into the host country’s economy through their spending on accommodation, food, transportation, and leisure activities. Unlike traditional tourists, they often stay for extended periods, contributing to a more consistent economic impact. Secondly, these individuals are typically highly skilled professionals, often working in sectors like technology, marketing, design, and consulting. Their presence can foster knowledge transfer, potentially leading to local innovation and entrepreneurship. Furthermore, by offering a welcoming environment for remote workers, countries can tap into a global talent pool, making them more attractive destinations for foreign investment and business relocation.
Statistics from various market research firms highlight the scale of this trend. Projections indicate that the global digital nomad population, estimated to be in the tens of millions, is set to grow exponentially in the coming years. This growth is intrinsically linked to the availability and attractiveness of digital nomad visa programs. Countries that offer clear, accessible, and well-defined visa pathways, coupled with a supportive ecosystem—including reliable internet infrastructure, co-working spaces, and a reasonable cost of living—are poised to reap the greatest rewards.
The economic impact analysis for countries implementing these visas is increasingly positive. For instance, studies on the economic contribution of digital nomads in countries like Portugal have shown significant inflows of capital and a boost to local businesses, particularly in areas that were previously less reliant on international tourism. These individuals often seek out destinations that offer a high quality of life, access to nature, and a vibrant cultural scene, thereby promoting the development of niche tourism sectors and supporting local artisans and service providers. The average spending of a digital nomad can significantly outweigh that of a short-term tourist, especially when considering their longer stays and consistent income streams.
However, the implementation of these programs is not without its challenges and nuances. Concerns often arise regarding housing affordability for local populations, potential strain on public services, and the need for robust tax frameworks to ensure fair contribution. Successful digital nomad visa programs must therefore be carefully designed to mitigate these potential negative externalities. This includes measures such as setting income thresholds for applicants, encouraging longer-term accommodation leases, and establishing clear guidelines for taxation. Furthermore, the long-term sustainability of these programs hinges on a country’s ability to integrate digital nomads into the local community, fostering mutual understanding and respect.
The competitive landscape for digital nomad visas is intensifying. Nations are differentiating themselves through various incentives and program features. Some offer expedited application processes, tax breaks for specific income brackets, or dedicated support services for arriving nomads. The ease of visa application and renewal is also a critical factor. Countries that streamline bureaucratic processes and offer clear communication channels are more likely to attract and retain digital nomads. The legal frameworks surrounding these visas are also evolving, with many countries moving beyond simple tourist visa extensions to create bespoke residency permits tailored to the needs of remote workers.
Looking ahead to 2025 and beyond, the trend of countries actively pursuing digital nomad visa policies is expected to accelerate. This reflects a broader global shift towards recognizing the economic and social benefits of a mobile, skilled workforce. As more governments understand the potential for talent attraction, foreign investment, and economic diversification, the number and variety of digital nomad visa offerings will undoubtedly continue to expand. This evolving policy environment presents both opportunities and challenges for individuals seeking to embrace the digital nomad lifestyle, and for nations aiming to position themselves as leading destinations in this new era of global work. The strategic deployment of digital nomad visas is no longer a niche policy; it is becoming a crucial component of national economic development strategies worldwide.