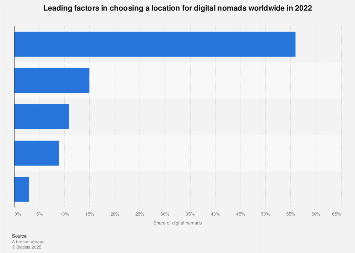
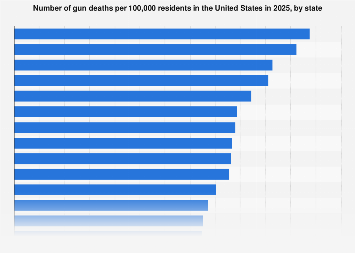
The burgeoning digital nomad lifestyle, characterized by the freedom to work remotely from virtually anywhere, hinges on a delicate balance of essential factors when choosing a destination. In 2022, the siren call of new adventures and the inherent flexibility of modern technology propelled this demographic to the forefront of global mobility. For this cohort, a stable internet connection and affordability emerged as the paramount considerations, underpinning their ability to maintain productivity and manage their finances effectively. This trend highlights a fundamental shift in how individuals perceive work and life, with location no longer being an immutable constraint but rather a curated choice.
Beyond the immediate practicalities of connectivity and cost, personal safety ranked as a significant deterrent or draw for a substantial portion of the digital nomad community. This emphasis on security underscores a nuanced understanding of location, where the allure of exotic locales must be tempered with the assurance of personal well-being. The data, derived from a survey of 4,000 respondents conducted online, provides a granular view into the decision-making matrix of these modern-day explorers. While the precise survey dates are not specified, the findings offer a valuable snapshot of prevailing preferences and priorities within the digital nomad ecosystem during that period.
The economic implications of these preferences are far-reaching. Destinations that can effectively address these core needs – robust internet infrastructure, a favorable cost of living, and a demonstrably safe environment – are poised to attract a significant influx of mobile talent and their associated spending power. This creates a competitive landscape for cities and countries seeking to capitalize on the digital nomad trend, fostering an environment of innovation in infrastructure development and local amenities.
Examining the broader economic context, the rise of digital nomadism is intrinsically linked to the acceleration of remote work adoption, catalyzed by global events and technological advancements. Companies worldwide have increasingly embraced flexible work arrangements, empowering employees to transcend geographical limitations. This shift has not only democratized access to global talent pools but has also spurred the growth of the "digital nomad economy," encompassing co-working spaces, short-term rentals, and localized service industries catering to this transient workforce.
The cost of living, a primary driver for digital nomads, is a complex metric influenced by a multitude of factors including housing, food, transportation, and leisure activities. Countries with a lower cost of living, particularly in Southeast Asia, Eastern Europe, and Latin America, have historically been popular choices. For instance, cities like Chiang Mai in Thailand, Lisbon in Portugal, and Medellín in Colombia have established themselves as vibrant hubs for digital nomads, offering an attractive combination of affordability and lifestyle. However, the definition of "affordable" is subjective and can vary based on individual spending habits and the desired level of comfort.
Internet connectivity, the lifeblood of any remote worker, is no longer a luxury but a fundamental necessity. Fast, reliable, and widely accessible internet is a non-negotiable requirement. This has led to an increased demand for destinations with well-developed digital infrastructure, including widespread fiber optic networks and readily available Wi-Fi hotspots. Emerging technologies like 5G are further enhancing the viability of remote work, promising even greater speeds and lower latency, which are crucial for activities such as video conferencing, cloud computing, and real-time collaboration. The global disparity in internet access, however, remains a significant barrier for many aspiring digital nomads, highlighting the ongoing need for investment in digital infrastructure in developing regions.
Safety, as indicated by the survey, is a critical factor that influences the desirability of a location. This encompasses not only low crime rates but also political stability, public health infrastructure, and a general sense of security. Destinations that can demonstrate a commitment to these aspects are more likely to attract and retain digital nomads. This concern for safety is particularly pronounced for individuals who may be traveling solo or are responsible for their own well-being in unfamiliar environments. International organizations and local governments that prioritize citizen safety and provide clear information about local conditions can significantly enhance their appeal.
The pursuit of community and social connection also plays a role, albeit often secondary to the core practicalities. Digital nomads, while valuing independence, often seek opportunities to connect with like-minded individuals, share experiences, and build professional networks. Cities with a strong existing digital nomad community, co-working spaces, and organized social events tend to foster a sense of belonging and facilitate integration. This aspect underscores the evolving nature of work, where social capital and peer support are increasingly recognized as valuable components of professional success and personal fulfillment.
Comparing global trends, it is evident that the digital nomad movement is not monolithic. Different regions and countries offer distinct advantages. For instance, Western Europe, while generally more expensive, often boasts superior infrastructure, ease of travel within the Schengen Area, and a high standard of living. Conversely, parts of Asia and Latin America offer a significantly lower cost of living, allowing digital nomads to stretch their budgets further and potentially invest more in experiences and personal development.
The economic impact of digital nomads extends beyond their direct spending. They contribute to local economies through taxes, consumption of goods and services, and the creation of demand for specialized services like co-working spaces and property rentals. Furthermore, their presence can foster innovation and entrepreneurship by bringing new ideas and perspectives to local communities. However, concerns have also been raised regarding the potential impact of a large influx of digital nomads on local housing markets and the cost of living for permanent residents, necessitating thoughtful urban planning and policy interventions.
The long-term sustainability of the digital nomad phenomenon will depend on a variety of factors, including the continued evolution of remote work policies, the development of digital infrastructure globally, and the ability of destinations to adapt to the unique needs of this mobile workforce. As technology continues to advance and the perception of work undergoes a fundamental transformation, the digital nomad lifestyle is likely to become even more prevalent, reshaping global mobility and the very definition of a "workplace." The insights gleaned from the 2022 data provide a crucial foundation for understanding the current landscape and anticipating future trends in this dynamic and ever-evolving sector of the global economy.