The contemporary business landscape demands a leadership paradigm rooted in unwavering authenticity and a keen awareness of evolving operational and ethical complexities. As global markets oscillate and societal expectations for corporate responsibility intensify, executives face the dual challenge of remaining true to their core values while adeptly steering their organizations through turbulent waters. Insights from leading management research underscore that effective leadership in this era is not merely about perceived trustworthiness but about a deeply internalized commitment to principles that guide action, even when faced with significant pressure or technological disruption.
Authentic leadership, a concept widely lauded for its ability to foster trust and engagement, carries a nuanced "shadow side" that can undermine its very intent if not anchored in profound self-awareness. When leaders equate authenticity with the unbridled expression of their unfiltered selves, they risk becoming what some researchers term an "authentic jerk." This phenomenon, observed in executive coaching and leadership development studies, highlights a critical distinction: true authenticity is not merely about being oneself, but about aligning one’s actions with a clear understanding of what one stands for. A leader who operates from a place of unexamined ego or personal bias, rather than from a rigorously defined set of core values, can inadvertently alienate employees, erode morale, and damage organizational culture. The roadmap to constructive authenticity begins with rigorous introspection, identifying a personal and organizational "North Star" of values, and then diligently ensuring all decisions and behaviors are congruent with these guiding principles. This consistent, transparent effort to live by one’s values, especially during challenging times, is the bedrock upon which genuine trust is built, influencing everything from employee retention rates to market reputation.

Maintaining this alignment between corporate values and operational realities becomes particularly arduous amidst an increasingly polarized socio-political climate. Companies committed to environmental stewardship, diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI), or other progressive social objectives frequently find themselves caught in the crossfire of public debate. What was once considered responsible corporate citizenship can now be weaponized by critics, leading to accusations of "wokeness," consumer boycotts, and even legislative pushback. For instance, a recent survey indicated that over 60% of consumers globally expect brands to take a stand on social issues, yet a significant minority express skepticism or outright hostility towards such initiatives. This tension forces leaders to navigate a delicate balance: upholding deeply held commitments that resonate with employees and a substantial segment of stakeholders, without exposing the enterprise to undue business risk. Strategies for "quiet corporate activism" are emerging, advising leaders to steer through these storms by focusing on internal initiatives, transparently communicating the business rationale for values-driven decisions, and strategically engaging with stakeholders rather than engaging in performative public gestures. This measured approach can help organizations maintain fidelity to their ethical compass, protect their brand equity, and ensure long-term resilience.
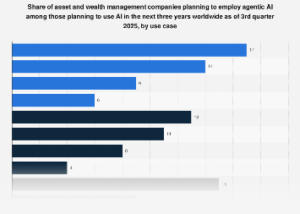
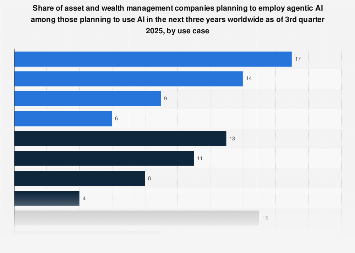
The advent and rapid proliferation of artificial intelligence (AI) across strategic and operational domains introduce a new frontier of ethical and practical risks that demand robust governance. While many organizations have embraced "responsible AI frameworks" and ethical principles, translating these guidelines into effective, day-to-day risk management remains a significant challenge. Industry reports suggest that despite the conceptual understanding of AI risks—such as algorithmic bias, data privacy breaches, and lack of transparency—many companies struggle with implementation. This lag is largely attributable to pervasive cultural and structural impediments within organizations. Siloed teams, a dearth of specialized training, and a lack of clear accountability for AI ethics often mean that ethical considerations become an afterthought, rather than an integral component of AI development and deployment lifecycle. To bridge this gap, leaders must establish clear roles and responsibilities for AI governance, invest in comprehensive training and tools for their teams, and embed ethical considerations directly into strategic decision-making processes. Failure to do so not only risks reputational damage and regulatory penalties but could also impede innovation and diminish competitive advantage in an AI-driven economy.
A particularly salient example of AI-related risk lies in algorithmic pricing, which has exposed companies to substantial legal scrutiny. The use of sophisticated algorithms to dynamically adjust prices in real-time has led to a surge of lawsuits alleging collusion and price-fixing. These legal challenges often target both the vendors of pricing algorithms and the companies that utilize them, particularly in sectors like multi-tenant residential real estate and hospitality. The core of these allegations often revolves around whether algorithms, designed to optimize profit, inadvertently facilitate or directly enable anti-competitive practices by coordinating pricing decisions across multiple, ostensibly independent, market players. The legal landscape here is complex, distinguishing between "conscious parallelism"—where competitors independently respond to market conditions in similar ways—and actual collusion, which is illegal. While some cases have seen settlements and others dismissed, many remain active, signaling a critical need for vigilance. The economic implications of such lawsuits can be severe, ranging from hefty fines and mandated operational changes to significant reputational harm and class-action settlements that collectively can amount to billions of dollars. Companies considering or currently employing AI for pricing decisions must monitor these legal developments closely, seeking expert counsel to understand the intricate nuances of antitrust law and proactively implement robust internal controls, transparency mechanisms, and independent audits to mitigate legal exposure.

Ultimately, the future of successful leadership hinges on an integrated approach to integrity. It requires leaders to cultivate deep self-awareness to prevent authenticity from devolving into counterproductive behavior. It demands strategic acumen to uphold core values in the face of political and societal pressures, transforming potential backlash into opportunities for meaningful stakeholder engagement. And it necessitates proactive governance and continuous education to harness the transformative power of AI while rigorously mitigating its inherent risks. The convergence of these challenges underscores that leadership is no longer just about optimizing profits, but about safeguarding principles, ensuring ethical conduct, and fostering a resilient, trustworthy enterprise that can thrive amidst unprecedented complexity.