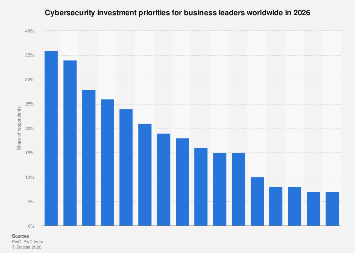
As businesses worldwide brace for an increasingly complex and dynamic threat landscape, strategic investment in cybersecurity is paramount. Emerging data indicates that by 2026, business leaders are overwhelmingly prioritizing Artificial Intelligence (AI) and cloud security as their primary defensive fortresses. A comprehensive survey of 3,887 business leaders, conducted between May and July 2025, reveals a clear strategic direction, with AI emerging as the top investment priority for 36 percent of respondents, closely followed by cloud security at 34 percent. This focus underscores a significant shift towards leveraging advanced technologies and securing the ubiquitous digital infrastructure that underpins modern commerce.
The strategic imperative to invest in AI within cybersecurity is multi-faceted. AI’s capabilities in threat detection, anomaly identification, and automated response are seen as critical to staying ahead of sophisticated cyber adversaries. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast datasets in real-time, identifying subtle patterns that human analysts might miss, thereby enabling proactive threat mitigation. This includes predicting potential breaches, identifying zero-day exploits, and automating routine security tasks, freeing up human talent for more complex strategic initiatives. The integration of AI is not merely about defense; it’s about creating a more intelligent, adaptive, and resilient security posture capable of evolving alongside emerging threats.
Cloud security, the second most prominent investment area, reflects the pervasive adoption of cloud computing across industries. As organizations migrate critical data and operations to the cloud, ensuring the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of these resources becomes a foundational requirement. Investments in this area will likely encompass a range of solutions, including enhanced identity and access management (IAM) for cloud environments, data encryption, secure configuration management, and continuous monitoring of cloud infrastructure. The distributed nature of cloud services necessitates a robust and adaptable security framework that can protect assets across multiple platforms and providers.
Beyond these leading priorities, a significant portion of business leaders are also focusing on bolstering core cybersecurity pillars. Network security and the implementation of zero-trust architectures are slated for investment by 28 percent of respondents. This indicates a strategic move away from traditional perimeter-based security models towards a more granular, identity-centric approach that verifies every access request, regardless of origin. Data protection and data trust initiatives are also high on the agenda, with 26 percent of leaders planning to invest in these areas, highlighting the ongoing importance of safeguarding sensitive information against breaches and ensuring data integrity.
Threat management, a broad category encompassing threat intelligence, incident response, and vulnerability management, is a priority for 24 percent of surveyed leaders. This reflects a continuous effort to improve an organization’s ability to anticipate, detect, and respond to cyber threats effectively. The increasing reliance on cyber managed services by 21 percent of businesses suggests a growing trend towards outsourcing specialized security functions, allowing organizations to leverage external expertise and resources to address complex security challenges.
The survey also sheds light on other key investment areas. Security awareness training, crucial for mitigating human error which often serves as an entry point for attackers, is a priority for 19 percent of leaders. This highlights the recognition that technology alone is insufficient and that a well-informed workforce is a vital component of a comprehensive security strategy. Identity and Access Management (IAM), fundamental for controlling user access to systems and data, is targeted by 18 percent of respondents.
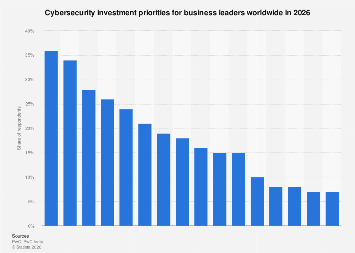
Further down the list, but still significant, are investments in supply chain and third-party risk management (16 percent), and endpoint security (15 percent). The increasing interconnectedness of business operations means that vulnerabilities in a partner’s systems can pose a direct threat. Therefore, scrutinizing and securing the entire supply chain is becoming a critical aspect of enterprise security. Endpoint security, focusing on protecting devices like laptops, smartphones, and servers, remains a persistent concern. Application security, another area receiving 15 percent of investment focus, underscores the need to build secure software from the ground up and protect applications from exploitation.
Operational technology (OT) security, essential for industries relying on industrial control systems and critical infrastructure, is a priority for 10 percent of leaders. As these systems become increasingly digitized and connected, their vulnerability to cyberattacks grows, necessitating dedicated security investments. Connected products and mobile security, while lower on the overall priority list at 8 percent and 7 percent respectively, still represent areas of concern, especially for companies with extensive IoT deployments or those heavily reliant on mobile workforces.
Interestingly, quantum computing, a field with immense long-term potential for both cybersecurity threats and solutions, is currently a low-priority investment for most business leaders, with only 8 percent identifying it as a top focus. Similarly, API security, a critical component for modern application development and integration, is a priority for just 7 percent. This suggests that while the long-term implications of quantum computing are recognized, the immediate and pressing needs related to AI, cloud, and foundational security practices are taking precedence in current investment cycles. The relatively low emphasis on API security, despite its increasing importance in a microservices-driven world, may indicate a gap in understanding or a deferred investment strategy.
The global cybersecurity market is projected to witness substantial growth in the coming years, driven by these investment trends. Analysts predict the market to reach hundreds of billions of dollars by the end of the decade. The sustained rise in cyberattacks, coupled with increasingly stringent regulatory frameworks and the growing complexity of IT infrastructures, are key catalysts for this expansion. The focus on AI and cloud security aligns with broader economic trends, such as digital transformation, remote work, and the proliferation of data.
However, this investment landscape is not without its challenges. The skills gap in cybersecurity remains a significant hurdle. The demand for skilled professionals in areas like AI-driven security analysis, cloud security architecture, and threat intelligence often outstrips supply. This necessitates not only investment in technology but also in talent development and training programs to equip the workforce with the necessary skills to manage and leverage these advanced security solutions.
Furthermore, the evolving nature of cyber threats means that security strategies must be agile and adaptable. The rise of sophisticated ransomware attacks, state-sponsored cyber espionage, and increasingly complex supply chain attacks require continuous reassessment of priorities and investment. The emphasis on AI and cloud security for 2026 suggests a proactive approach, but the success of these investments will depend on their effective implementation, integration with existing security frameworks, and the ability of organizations to continuously monitor and adapt their defenses in response to emerging threats. The data from this survey provides a valuable snapshot of business leaders’ strategic thinking, guiding the trajectory of cybersecurity investments and shaping the global defense against digital risks in the years to come.