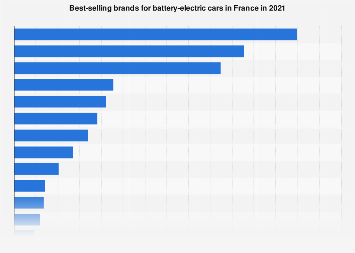
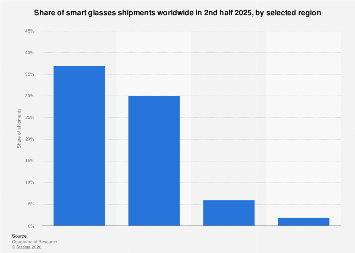
The year 2021 marked a pivotal moment for the French automotive sector, as battery electric vehicles (BEVs) continued their upward trajectory, reshaping market share and consumer preferences. While the broader automotive industry grappled with persistent supply chain disruptions, particularly the global semiconductor shortage, the BEV segment demonstrated remarkable resilience and growth. Analysis of sales data from that year reveals a complex landscape, with established manufacturers vying for dominance against emerging players, underscoring the evolving competitive environment in one of Europe’s largest car markets.
Globally, 2021 saw a surge in BEV adoption, driven by a confluence of factors. Stricter emissions regulations across major economies, substantial government incentives, and a growing consumer awareness of environmental sustainability propelled the transition away from internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. In France, these global trends were amplified. The French government, through its "Plan Véhicule Électrique" and various bonus schemes like the "bonus écologique," actively encouraged the purchase of zero-emission vehicles. These policies, coupled with a broader societal shift towards greener mobility solutions, created a fertile ground for BEV sales to flourish.
Examining the brand-level performance in France for 2021 offers a granular perspective on these market shifts. While specific figures are proprietary and subject to licensing, the general trends indicate a dynamic interplay between traditional automotive giants and newer, more specialized electric vehicle manufacturers. The established European automakers, with their extensive dealer networks and brand recognition, made significant strides in electrifying their lineups. Their efforts to introduce a wider range of BEV models, from compact city cars to larger SUVs, resonated with a diverse consumer base. This strategic pivot was crucial, as it allowed them to leverage existing customer loyalty while appealing to a new demographic of environmentally conscious buyers.
However, the market was not solely dominated by legacy players. Dedicated electric vehicle manufacturers, often characterized by their technological innovation and focused product offerings, also carved out significant market share. These companies, frequently originating from outside Europe, brought fresh perspectives and advanced battery technology to the forefront, challenging conventional automotive design and performance benchmarks. Their agility in responding to market demands and their commitment to all-electric platforms often allowed them to capture early adopters and build a strong following among tech-savvy consumers. The competition between these two distinct groups fostered a more dynamic and innovative market, ultimately benefiting consumers through increased choice and improved product offerings.
The growth in BEV sales in France during 2021 was not uniform across all segments of the market. The passenger car segment, in particular, witnessed substantial gains. This was partly attributable to the availability of smaller, more affordable BEVs, which are ideal for urban commuting and align with the purchasing power of a wider segment of the population. The increasing range of these vehicles, coupled with the expanding charging infrastructure, helped to alleviate range anxiety, a key barrier to adoption in previous years. Furthermore, the expansion of electric versions of popular SUV models tapped into a growing consumer preference for larger vehicles, demonstrating that the transition to electric mobility was not limited to niche segments.
Beyond passenger cars, the commercial vehicle sector also saw a notable uptick in BEV adoption. Fleet operators, including delivery services and logistics companies, began to recognize the long-term cost savings associated with electric powertrains, such as lower fuel and maintenance expenses. Government regulations aimed at reducing emissions in urban centers further incentivized businesses to electrify their fleets. This growing demand from the commercial sector not only contributed to overall BEV sales figures but also played a crucial role in normalizing the presence of electric vehicles on French roads.
The economic implications of this BEV sales surge were multifaceted. For the French automotive industry, it signaled a necessary but challenging transition. Manufacturers and their supply chains had to invest heavily in research and development, retooling production facilities, and retraining their workforce. The shift presented opportunities for domestic battery manufacturers and charging infrastructure providers, fostering job creation and technological advancement within the country. Conversely, it also posed a threat to traditional component suppliers heavily reliant on ICE technology, necessitating diversification and adaptation.
On a national economic level, the increased adoption of BEVs contributed to France’s efforts to meet its climate targets and reduce its reliance on fossil fuels. The reduction in tailpipe emissions, particularly in urban areas, promised improvements in air quality and public health. Furthermore, the government’s investment in charging infrastructure and battery production aimed to position France as a leader in the burgeoning green economy, attracting foreign investment and fostering export opportunities.
However, challenges remained. The upfront cost of BEVs, while decreasing, was still a significant factor for many consumers, making government subsidies indispensable. The pace of charging infrastructure deployment, while accelerating, needed to keep pace with the growing number of electric vehicles to ensure convenience and widespread adoption. The sourcing of raw materials for batteries and the ethical considerations surrounding their extraction also emerged as critical issues for long-term sustainability.
Looking ahead, the trends observed in 2021 laid the groundwork for continued BEV growth in France. The commitment to electrification was evident in the product pipelines of all major manufacturers, with new and improved models continuously entering the market. The ongoing refinement of battery technology promised longer ranges and faster charging times, further enhancing the appeal of electric vehicles. As the market matured and economies of scale took hold, it was anticipated that BEVs would become increasingly competitive with their ICE counterparts on price, further accelerating the transition. The competitive landscape, characterized by both established players and innovative newcomers, was expected to remain intense, driving further innovation and consumer benefits in the French electric vehicle market.